INSTRUCTIONS FOR COLONOSCOPY
Key Points for your colonoscopy prepping. For more information please read the whole package:
Medications for the preparation:
- - 4 Tablets of Dulcolax
- - 1 Gallon of NuLYTELY or similar products. Less liquid colonoscopy preps are available, most often does not get coverage from insurance company. If you are interested, please ask your procedure coordinator.
Please inform your procedure coordinator if you are on the following:
- - Blood thinner (aspirin, aleve, motrin, plavix, coumadin…)
- - Have any heart conditions
- - Take any medications in the morning
Day before your colonoscopy:
- - NO FOOD. Stay on a clear liquid diet. No Solid Food! Stay closed to the bathroom
- - NO RED or PURPLE products.
- - At 1:00 pm take 2 tablets of Dulcolax
- - At 3:00 pm take 2 additional tablets of Dulcolax
- - Start drinking the solutions. Drink 8 ounces of solution every 10-15 minutes. Sip it like tea. Drinking it too fast will result in vomiting.
- - Immediately right after the second dosages of Dulcolax, begin drinking the 1st half of the solution as directed above until you finish half.
- - At 9:00 pm start drinking the 2nd haft as directed above until you finish the whole entire bottle.
- - DO NOT eat or drink after midnight.
- - No Alcohol
Day of your Colonoscopy:
- - Nothing to eat or drink unless it was approved by the doctor. If you have any questions about your medications, please ask your procedure coordinator.
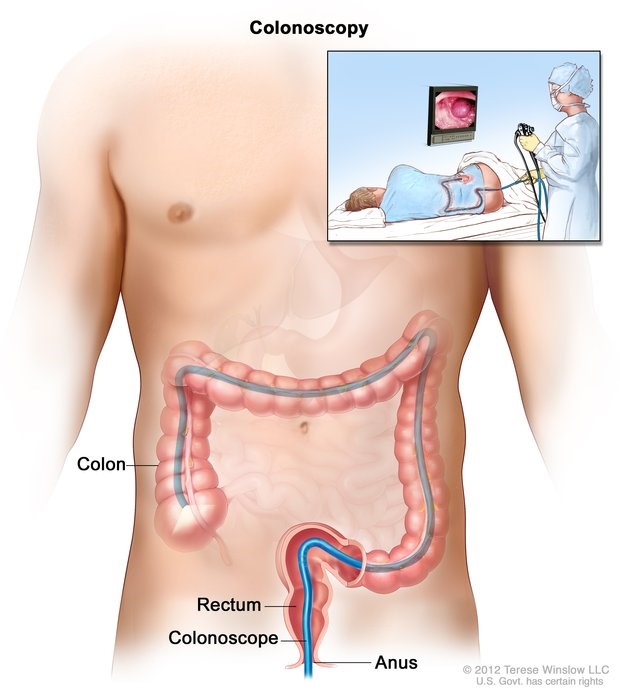
COLONOSCOPY
Overview:
The average lifetime risk of getting colorectal cancer is approximately 1 in 22 men and 1 in 24 women. Colorectal cancers are the second leading cause of cancer death in the United States. Many of these deaths can be prevented by getting early, regular screenings.
A colonoscopy is a screening test used to detect and prevent colon and colorectal cancers. Colonoscopies are also tools that can help determine the cause of gastrointestinal conditions, such as: chronic diarrhea or constipation and rectal or abdominal bleeding.
It’s recommended that people with average cancer risk start getting this test at age 45 or 50, and every 10 years afterward, through age 75.
Your family history and race may affect your risk of getting colon or colorectal cancer. Certain conditions may also increase your risk, such as:
- history of polyps in the colon
- Crohn’s disease
- inflammatory bowel disease
- ulcerative colitis
Talk to a doctor about your specific risk factors while determining when and how often you should have a colonoscopy. Nothing in life is without some level of risk, including this procedure. However, colonoscopies are done every day and are considered safe. While serious complications and even death may occur as a result of colonoscopy, your chances of getting colon or colorectal cancer far outweigh these possibilities.
Despite what you may have heard, preparing for and having a colonoscopy aren’t especially painful. Your doctor will give you specific instructions on how to get ready for the test.
Bowel prep is essential. It’s used to ensure that your colon is completely free of waste, providing your doctor with a clear view during the colonoscopy.
Colonoscopies are done either under twilight sedation or general anesthesia. As with any surgery, your vital signs will be monitored throughout. A doctor will insert a thin flexible tube with a video camera at its tip into your rectum.
If any abnormalities or precancerous polyps are seen during the test, your doctor will most likely remove them. You may also have tissue samples removed and sent for biopsy.
Colonoscopy risks
According to the American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, serious complications occur in around 2.8 percent of every 1,000 procedures when done in people of average risk.
If a doctor removes a polyp during the test, your chances of complications may increase slightly. While exceedingly rare, deaths have been reported following colonoscopies, primarily in people who had intestinal perforations occur during the test.
Choosing the outpatient facility where you have the procedure may impact your risk. One study showed a marked difference in complications, and quality of care, among facilities.
Risks associated with colonoscopy include:
Perforated intestine
Intestinal perforations are tiny tears in the rectum wall or colon. They can be made accidentally during the procedure by an instrument. These punctures are slightly more likely to occur if a polyp is removed.
Perforations can often be treated with watchful waiting, bed rest, and antibiotics. Large tears are medical emergencies that require surgical repair.
Bleeding
If a tissue sample is taken or a polyp removed, you may notice some bleeding from your rectum or blood in your stool a day or two after the test. This is typically nothing to be worried about. However, if your bleeding is heavy, or doesn’t stop, let your doctor know.
Post-polypectomy electrocoagulation syndrome
This rare complication can cause severe abdominal pain, rapid heart rate, and fever after a colonoscopy. It’s caused by an injury to the bowel wall which results in a burn. These rarely require surgical repair and can usually be treated with bed rest and medication.
Adverse reaction to anesthetic
All surgical procedures carry some risk of negative reactions to anesthesia. These include allergic reactions and respiratory distress.
Infection
Bacterial infections, such as E. coli and Klebsiella, have been known to occur after colonoscopy. These may be more likely to happen at medical centers that have inadequate infection control measures put in place.
Colonoscopy risks for older adults
Because colon cancer grows slowly, colonoscopies aren’t always recommended for people of average risk or who are older than 75, provided they had the test at least once during the last decade. Older adults are more likely than younger patients to experience complications or death after this procedure.
The bowel prep used can sometimes be of concern for seniors because it can lead to dehydration or electrolyte imbalance. People with left ventricular dysfunction or congestive heart failure may react poorly to prep solutions containing polyethylene glycol. These may increase intravascular water volume causing complications such as edema.
Prep drinks containing sodium phosphate might also cause kidney complications in some older people.
It’s vital that older people completely understand their colonoscopy prep instructions and are willing to drink the full amount of prep liquid required. Not doing so could result in lower completion rates during the test.
Based on underlying health conditions and health history in older adults, there can also be an increased risk for heart- or lung-related events in the weeks following a colonoscopy.
Problems after colonoscopy
You’ll most likely be tired after the procedure. Since anesthesia is used, you may be required to have someone else take you home. It’s important to watch what you eat after the procedure so as not to irritate your colon and to avoid dehydration.
Postprocedure problems may include:
- feeling bloated or gassy if air is introduced into your colon during the procedure and it starts to leave your system
- a slight amount of blood coming from your rectum or in your first bowel movement
- temporary light cramping or abdominal pain
- nausea as a result of the anesthesia
- rectal irritation from the bowel prep or the procedure
Any symptom that causes concern is a good reason to call a doctor.
These include:
- severe or prolonged abdominal pain
- fever
- chills
- severe or prolonged bleeding
- rapid heart rate
Alternatives to a traditional colonoscopy
Colonoscopy is considered the gold standard of screening tests for colon and rectal cancers. However, there are other types of tests that might be appropriate for you. These tests typically require colonoscopy as a follow-up if abnormalities are uncovered. They include:
- Fecal immunochemical test. This at-home test checks for blood in the stool and must be taken annually.
- Fecal occult blood test. This test adds a blood test component to the fecal immunochemical test and also must be repeated annually.
- Stool DNA. This at-home test analyzes stool for blood and for DNA that might be associated with colon cancer.
- Double-contrast barium enema. This in-office X-ray also requires prior bowel cleansing prep. It can be effective at identifying large polyps but may not detect smaller ones.
- CT colonography. This in-office test also uses bowel cleansing prep but does not require anesthesia.
List of Aspirin or Aspirin Related Drugs
4-Way Cold Tablets
Adprin - B Tablets
A.S.A. Enseals
A.S.A. Tablets
Aches-N Pain Tablets
Advil
Alcohol
Aleve Tablets
Alka-Seltzer Products
Amigesic capsules
Anacin Tablets and Capsules
Anaprox, Anaprox DS Tablets
Anodynos Tablets
Ansaid Tablets
APC
Argesic Tablets
Artha-G Tablets
Arthralgen Tablets
Arthritis Bayer Timed Release Aspirin
Arthritis Pain Formula Tablets
Arthritis Strength Buffering Tablets
Arthropan Liquid
Arthrotec
Ascodeen
Ascriptin, All products
Asperbuf Tablets
Aspergum [chewing gum]
Aspirin
Asprimox Tablets
Axdone
Axotal Tablets
Bayer, All products
BC Tablets and Powder
Brufen
Buf-Tabs
Buff-A Comp No. 3 Tablets with codeine
Buff-A Comp Tablets and Capsules
Buffaprin Tablets
Bufferin, All products
Buffets II Tablets
Buffex Tablets
Buffinol Tablets
Cama Arthritis Pain Relieve
CataFlam Tablets
Cephalgesis
Cheracol
Children Aspirin
Children's Advil Suspension
Children's Motrin Suspension
Congesprin
Cope Tablets
Coricidin
Coumadin
Darvon Compound Pulvules
Darvon with A.S.A. Pulvules
Darvon Compound-65
Darvon-N with A.S.A.
Dasin Capsules
Daypro Tablets
DiFlunisal
Disalcid Capsules
Doan’s Pills
Dolobid Tablets
Dristan
Duoprin-S Syrup
Duradyne Tablets
Easprin
Ecotrin Tablets
Emagrin Tablets
Empirin Tablets
Emprazil
Endodan Tablets
Epromate Tablets
Equagesic Tablets
Equazine M Tablets
Etodolac
Excedrin Tablets and Capsules
Feldene Capsules
Fenoprofen Tablets
Fiorgen PF Tablets
Fiorinal Tablets
Fluriprofen Tablets
Gelpirin Tablets
Gensan Tablets
Goody's Headache Powder
Halfprin Tablets
Haltran Tablets
Ibu-Tab Tablets
Ibuprin Tablets
Ibuprohm Tablets and Caplets
Indochron E-R Capsules
Indocin Capsules/Suspension/ Suppositories
Indocin-SR Capsules
Indomethacin Capsules
Indomethacin Suspension
Isollyl Improved Tablets & Capsules
Ketrolac Tablets
Ketoprofen Capsules
Lanorinal Tablets
Lodine Capsules /Tablets
LodineXL
Lortab
Magan Tablets
Magnaprin Arthritis Strength Captabs
Magsal Tablets
Mamal Capusles
Marthritic Tablets
Maximum Bayer Aspirin
Measurin Tablets
MecloFenamate Capsules
Meclomen Capsules
Medipren Tablets and Caplets
Menadol Tablets
Meprogesic Tablets
Micrainin Tablets
Midol 200 Tablets
Midol, All products
Mobidin Tablets
Mobigesic Tablets
Momentum Tablets
Motrin Tablets
Nalfon Capsules/Tablets
Nalfon Pulvules
Naprosyn Tablets/Suspension
Naproxen Tablets
Neocylate Tablets
Norgesic & Norgesic Forte Tablets
Norwich Extra-Strength Tablets
Nuprin Tablets and Caplets
Orphengesic
Orudis Capsules
Oruvail Capsules
Pabalate
Pabalate-SF Tablets
PAC Tablets
Pamprin-IB Tablets
Pepto-Bismol Tablets and Suspension
Percodan and Percodan Demi Tablets
Phenaphen
Piroxicam Capsules
Ponstel Capsules
Presalin Tablets
Relafen Tablets
Robaxisal Tablets
Rufen Tablets
S-A-C
Saleto Tablets Capsules,
Saleto-200 Tablets
Saleto-400,600,800 Tablets
SalFlex Tablets
Salocol Tablets
Salsalate Tablets
Salsitabs Tablets
Sine-Aid
Sine-Off
SK-65 Compound Capsules
Soma
Soma CMD
St. Joseph Adult Chewable Aspirin
St. Joseph Cold Tablets for Children
St. Joseph Aspirin for Children
Sulindac Tablets
Supac
Synalgos Capsules
Synalgos-DC Capsules
Talwin Compound Tablets
Tolectin 200,600 Tablets
Tolectin DS Capsules
Tolmetin Tablets/Capsules
Toradol
Injection/Tablets
Trendar Tablets
Tricosal Tablets
Tri-Pain Tablets
Trigesic
Trigesic Tablets
Trilisate Tablets and Liquid
Vanquish Caplets
Verin
Voltaren Tablets
Zactin
Zorprin Tablets
CLEAR LIQUID DlET
This diet provides fluids that leave little residue and are easily absorbed with minimal digestive activity. This diet is inadequate in all essential nutrients and is recommended only if clear liquids are temporarily needed.

Milk & beverages
- Foods Allowed:
- Tea (decaffeinated or regular)
- Carbonated beverages
- Fruit flavored drinks
- Foods to Avoid:
- Milk
- Milk drinks

Meats & Meat Substitutes
- Foods Allowed:
- None
- Foods to Avoid:
- All

Vegetables
- Foods Allowed:
- None
- Foods to Avoid:
- All

Fruits & Fruit Juices
- Foods Allowed:
- Strained fruit juices: apple, white grape, orange
- Foods to Avoid:
- Fruit juices with unstrained fruit

Grains & Starches
- Foods Allowed:
- None
- Foods to Avoid:
- All

Soups
- Foods Allowed:
- Clear broth
- Consommé
- Foods to Avoid:
- All others

Desserts
- Foods Allowed:
- Clear flavored gelatin
- popsicles, (no red flavors)
- Foods to Avoid:
- All others

Fats
- Foods Allowed:
- None
- Foods to Avoid:
- All

Miscellaneous
- Foods Allowed:
- Sugar, honey, syrup
- Clear hard candy
- Salt
- Foods to Avoid:
- All others
BREAKFAST
- 4 oz. White grape juice
- 6 oz. broth
- Jell-0
- Tea
LUNCH
- 4 oz. Apple juice
- 6 oz. broth
- Jell-0
- Tea
DINNER
- 4 oz. Orange juice (strained)
- 6 oz. broth
- Jell-0
- Tea
North Broward
201 East Sample Rd
Pompano Beach, FL
(954) 941-8300
Coral Springs Medical Center
3000 NW 96th Ave
Coral Springs, FL 33065
(954) 344-3000
Broward General Medical Center
1600 S Andrews Ave
Fort Lauderdale, FL 33316
(954) 355-4400
Surgery Center at Coral Springs
967 North University Drive
Coral Springs, FL 33071
(954) 509-1367
Northwest Medical Center
2801 N State Rd 7
Margate, FL 33063
(954) 974-0400
Boca Outpatient Surgical Center
501 Glades Road
Boca Raton, FL 33432
(561) 367-6090